GUILLAINE-BARRE SYNDROME (GBS) – CNS disorder characterized by bilateral,
symmetrical, polyneuritis leading to ascending muscle weakness/paralysis.
This blog is specially made for all NURSING professionals here in the Philippines and abroad. This contain nursing lectures and examination for nursing students that can be use for their board exam review..... This blog also post latest news, trends, research studies, jobs openings and all other articles pertaining to nursing profession....
Pages
▼
Sunday, November 25, 2012
Saturday, November 24, 2012
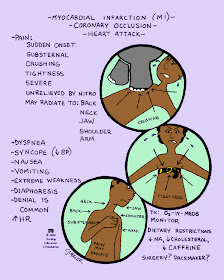
MS: Myocardial Infarction
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
- Death of myocardial cells from inadequate oxygenation, often caused by sudden complete blockage of a coronary artery
- Characterized by localized formation of necrosis (tissue destruction) with subsequent healing by scar formation & fibrosis
- Heart attack
- Terminal stage of coronary artery disease characterized by malocclusion, necrosis & scarring.
MS: COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), also known as chronic obstructive lung disease (COLD), chronic obstructive airway disease (COAD), chronic airflow limitation (CAL) and chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD), is the occurrence of chronic bronchitis or emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases of the lungs in which the airways narrow over time. This limits airflow to and from the lungs, causing shortness of breath (dyspnea). In clinical practice, COPD is defined by its characteristically low airflow on lung function tests. In contrast to asthma, this limitation is poorly reversible and usually gets progressively worse over time. In England, an estimated 842,100 of 50 million people have a diagnosis of COPD.
Wednesday, November 21, 2012
MS: Hypothyroidism vs Hyperthyroidism
HYPOTHYROIDISM
|
HYPERTHYROIDISM
|
Decreased T3 and T4
|
Increased T3 and T4
|
Early Signs
1.
Weakness and
fatigue
2.
Loss of appetite
but (+) weight gain d/t increased lipolysis
3.
Dry skin
4.
Cold intolerance
5.
Constipation
6.
Menorrhagia
Late Signs
1.
Brittleness of
hair
2.
Non-pitting
edema
3.
Hoarseness of
voice
4.
Decreased libido
5.
Decreased vs
6.
Cns changes
a.
Lethargy
b.
Memory
impairment
c.
Psychosis
|
1.
Hyperphagia
– increased appetite
2.
(+) weight loss
d/t increased metabolism
3.
heat intolerance
4.
moist skin
5.
diarrhea
6.
increased VS
7.
CNS changes
a.
Irritability
b.
agitation
c.
Tremors
d.
Restlessness
e.
Insomnia
f.
Hallucinations
8.
Goiter
9.
Exophthalmos
10.
Amenorrhea
|
1.
Monitor STRICTLY
VS, IO to determine presence of MYXEDEMA
COMA a complication of severe hypothyroidism characterized by:
a.
Severe
hypotension
b.
Bradycardia
c.
Bradypnea
d.
Hypoventilation
e.
Hypoglycemia
f.
Hyponatremia
g.
Hypothermia
2.
Administer
isotonic fluids as ordered
3.
Administer
medications as ordered – thyroid hormones or agents (may cause insomnia and
heat intolerance)
4.
Provide dietary
intake low in calories to prevent weight gain
5.
Institute
meticulous skin care
6.
Provide
comfortable and warm environment
7.
Forced fluids
|
1.
Monitor VS and
IO strictly to determine presence of THYROID
STORM/Crisis
2.
Administer
medications as ordered
a.
Anti-Thyroid
Agents: PTU à toxic effects is agranulocytosisà fever and chills, sore throat (throat CS pls!), leukocytosis (CBC pls!)
b.
Methimazole
(Tapazole)
3.
High calorie
diet to correct weight loss
4.
Provide
comfortable and cool environment
5.
Institute
meticulous skin care
6.
Maintain side
rails
7.
Bilateral eye
patch to prevent drying of eyes
8.
Assist in
surgical procedure: subtotal thyroidectomy
PRE-OP
Administer lugol’s solutions/ SSRI to promote decreased vasculature and promote atrophy of the thyroid gland to
prevent/minimize bleeding and hemorrhage
POST-OP
WOF signs of THYROID STORM à agitation, hyper-thermia, HPN. If (+) thyroid storm:
administer anti-pyretics and beta-blockers; VS, IO and NVS strictly,
siderails up, provide hypothermic blanket
WOF: inadvertent or accidental removal of parathyroid gland à hypocalcemia or tetany [(+) trousseu’s signs, (+)
chvostek’s Give Ca Gluc slowly to prevent arrhythmia and arrest
WOF accidental laryngeal nerve damage à hoarness of voice à instruct client to talk immediately post-op à if (+) notify MD
WOF signs of bleeding à (+) feeling of fullness at incision site, (+) soiled
dressings at back or nape area, notify MD
WOF signs of laryngeal spasm à DOB and SOB à prep trache set
9.
Hormonal
Replacement therapy for life
10.
importance of
FFup care
11.
wearing of
medic-alert bracelet
|
Monday, November 19, 2012
PNLE December 2012 UPDATES: NLE TIPS - MEDICAL AND SURGICAL NURSING
Dec 2012 NLE TIPS MS (A) from Mark Fredderick Abejo
DOWNLOAD PROCEDURE:
- LIKE us on Facebook via our FACEBOOK PAGE widget
- FOLLOW us on Twitter via our TWITTER ACCOUNT widget
- SHARE this blog on your own Facebook and Twitter account via SHARE IT widget
- POST your email address on the All For Nursing Facebook Page Wall
- CHECK your email regularly for the sent copy of this document.
NOTE: Widgets can be found on the right side portion of this BLOG / WEBSITE
THANK YOU SO MUCH.....
NEXT: DECEMBER 2012 NLE TIPS - PSYCHIATRIC NURSING
PNLE December 2012 UPDATES: NLE TIPS - COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
Dec 2012 NLE TIPS CHD and CD from Mark Fredderick Abejo
DOWNLOAD PROCEDURE:
- LIKE us on Facebook via our FACEBOOK PAGE widget
- FOLLOW us on Twitter via our TWITTER ACCOUNT widget
- SHARE this blog on your own Facebook and Twitter account via SHARE IT widget
- POST your email address on the All For Nursing Facebook Page Wall
- CHECK your email regularly for the sent copy of this document.
NOTE: Widgets can be found on the right side portion of this BLOG / WEBSITE
THANK YOU SO MUCH.....
NEXT: DECEMBER 2012 NLE TIPS - MS NURSING